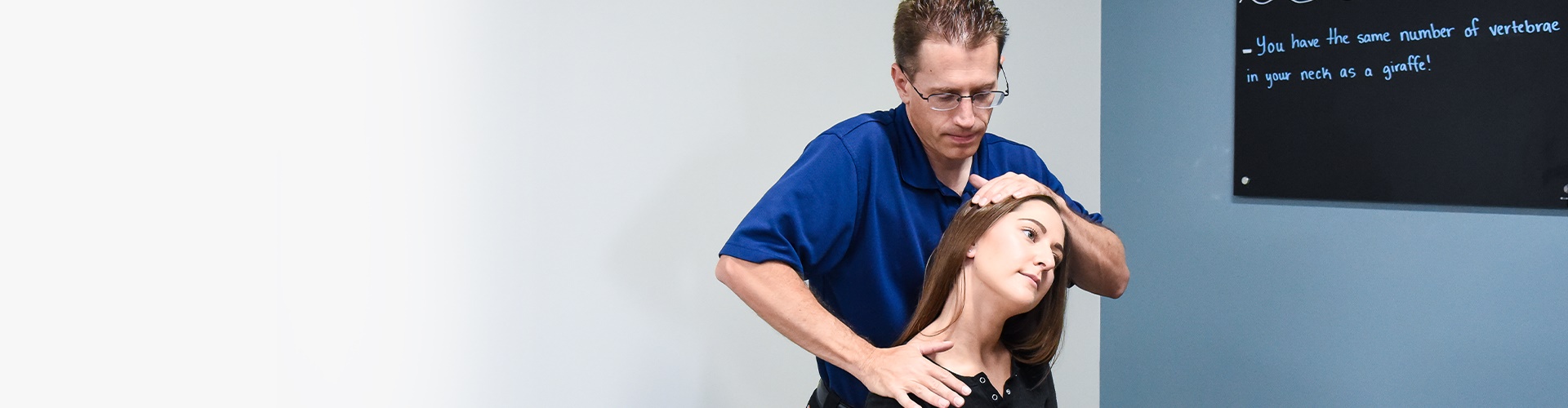
What Is Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
Myofascial Pain Syndrome is a chronic pain disorder characterized by the presence of trigger points—hyperirritable spots in the fascia (connective tissue) that can cause pain when compressed. These trigger points often develop due to muscle overuse, trauma, or stress.
What Are The Symptoms Of Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
Understanding and addressing the underlying issues related to Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) begins with recognizing its symptoms. Here’s an overview of the common indicators associated with MPS:
Localized Pain
Persistent, aching pain in specific muscle areas.

Muscle Stiffness
Difficulty moving certain muscles due to stiffness.

Tender Points
Touch-sensitive areas that may elicit pain when pressed.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Understanding the causes and risk factors of Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is fundamental for devising effective strategies in its prevention and management. This exploration provides valuable insights into the factors contributing to MPS, offering a foundation for tailored approaches that promote muscle health and overall well-being.
What Are The Causes?
Myofascial Pain Syndrome can arise from various factors:
-

Muscle Overuse: Repeated use or strain on particular muscles.
-
Trauma: Injuries, accidents, or surgeries that impact muscle function.
-

Stress: Emotional or physical stress contributing to muscle tension.
What Are The Risk Factors?
Explore the contributing factors to Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) in this section. Understanding these elements is crucial for proactive MPS prevention.
- Occupation: Jobs involving repetitive movements or prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Posture: Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances and trigger points.
- Lifestyle: Lack of exercise and poor stress management.
How Is Myofascial Pain Syndrome Diagnosed?
Discover methods for understanding Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS), from assessing muscle activity to deciphering pain patterns.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles. It can help identify abnormal muscle activity and detect the presence of trigger points.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans: These imaging techniques can reveal structural abnormalities, such as herniated discs or muscle damage, contributing to MPS symptoms.
- Manual Palpation: Skilled practitioners use their hands to palpate and identify areas of tenderness, tightness, or muscle abnormalities. This can provide valuable information about trigger points and muscle tension.
- Range of Motion (ROM) Assessment: Evaluating the range of motion in affected joints and muscles can help assess the impact of MPS on mobility and identify areas of restriction.
- Pain Mapping: Patients may be asked to keep a pain diary or use a pain mapping tool to document the location, intensity, and characteristics of their pain over time. This information can assist in identifying patterns and trigger points

How Can We Treat Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Discover effective treatments for Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS). From relieving pain to addressing root causes, this section explores diverse approaches to enhance well-being and reduce discomfort associated with MPS.
Discover the Ultimate Relief and Recovery Experience
With Highlands Family Chiropractic! Rely on our exceptional expertise for Myofascial Pain Syndrome Treatment.